Ancient art gives us a window into the minds and lives of early civilizations, revealing their beliefs, values, and unique artistic visions. The masterpieces left behind by ancient artists are more than just relics; they embody the history, spirituality, and everyday life of cultures that shaped human history. In this exploration, we will delve deep into the rich history of ancient art, understanding the techniques used, examining the significance of artistic expression in ancient civilizations, and reflecting on how ancient art continues to influence modern culture.
Understanding Ancient Art
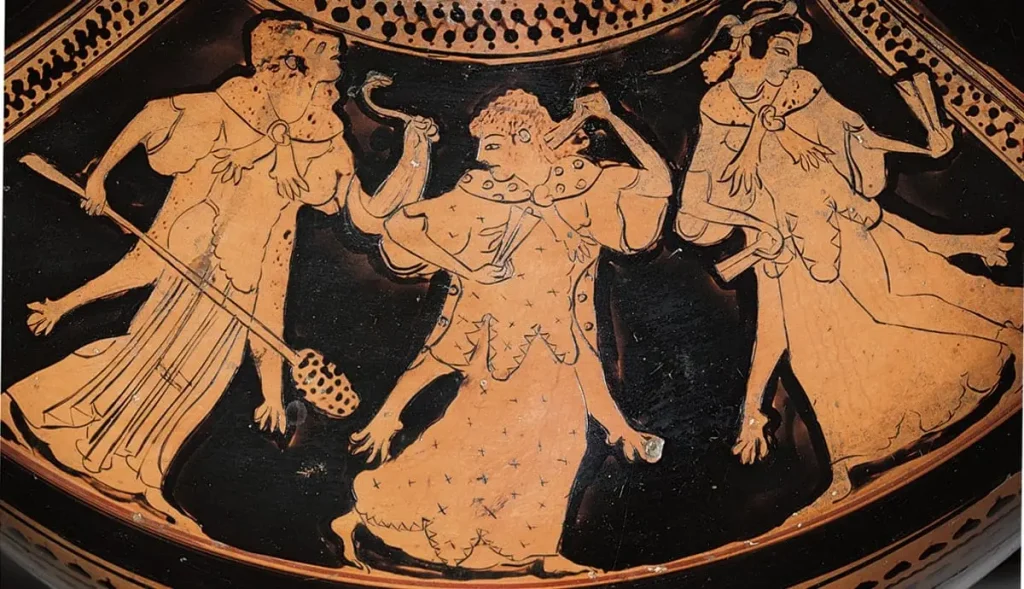
Ancient art encompasses the works created by civilizations from the dawn of human history through the early centuries AD, often categorized by the time period and cultural origin. Ancient art ranges from monumental architecture to intricate pottery, from powerful sculpture to delicate frescoes, and from painted cave walls to gold inlaid jewelry. But beyond the physical artifacts, ancient art serves as a lens into the lives, beliefs, and social structures of our ancestors.
While each ancient civilization had its unique style and symbolism, certain themes and artistic techniques recur across cultures. For example, the use of natural pigments, religious symbolism, and storytelling through visual imagery can be found in the art of Egypt, Greece, and Mesopotamia alike.
Key Ancient Civilizations in Art History
Ancient civilizations contributed immensely to the development of art and the techniques that defined it. Here are some notable cultures and their contributions:
Mesopotamian Art
Mesopotamian art reflects a blend of religious, political, and social themes. Known for their ziggurats, intricate carvings, and cylinder seals, the Mesopotamians developed one of the earliest written languages, cuneiform, which also influenced their artistic output. Depictions of gods and mythological figures were prevalent, showing their spiritual devotion.
Ancient Egyptian Art
Ancient Egyptian art is among the most iconic in history, marked by grand monuments like the Pyramids of Giza and the Sphinx, and by its detailed hieroglyphics. Egyptian art was heavily influenced by religion and the afterlife, with gods, pharaohs, and symbolism taking center stage in sculptures, paintings, and jewelry. The rigid, stylized forms of Egyptian art, with figures often shown in profile, reflect a highly ordered society with deep-rooted beliefs about life and death.
Greek and Roman Art
Greek art, particularly during the Classical period, is known for its pursuit of idealized beauty and balance, represented in sculpture, pottery, and architecture. The Greeks developed techniques for representing the human body in a realistic, anatomically accurate way, which had a profound influence on later Western art. Roman art built upon Greek techniques, but often focused more on realism and detail, especially in portraiture, mosaics, and monumental architecture like the Colosseum.
Mesoamerican Art
Ancient civilizations like the Maya, Aztec, and Olmec left behind impressive art and architectural achievements, including pyramids, temples, and intricate carvings. Mesoamerican art often featured religious and cosmological themes, with a strong emphasis on ritual and mythological symbolism. Mayan glyphs and Aztec codices are notable examples of complex iconography and storytelling.
Chinese and Indian Art
Ancient Chinese art spans from the Neolithic age through the Zhou and Han dynasties, with jade carvings, bronze casting, and ink paintings showcasing Chinese spirituality, philosophy, and social values. Indian art, exemplified by the Indus Valley Civilization and later Hindu and Buddhist art, often embodies religious symbolism, with temple sculptures and paintings depicting gods, goddesses, and cosmic themes.
Techniques and Materials in Ancient Art
Ancient art was shaped by the materials and tools available to each civilization. Artists of antiquity relied on natural materials, but they were highly innovative in creating a variety of effects and textures. Here are some prominent techniques:
Stone Carving and Sculpture
Stone was a primary medium for ancient artists, used for creating statues, stelae, and architectural reliefs. Techniques involved chiseling, sanding, and polishing, often requiring extensive labor. Greek and Roman artists, for instance, perfected the art of marble sculpture, while Egyptians preferred harder stones like granite for their monuments.
Fresco Painting
The fresco technique, popularized by the Minoans and later by the Romans, involves applying pigments to wet plaster, allowing the paint to become part of the wall surface. Frescoes adorned the interiors of buildings and temples, depicting scenes of daily life, mythology, and nature.
Pottery and Ceramics
Pottery was both an artistic and practical craft, with each culture developing distinct styles and methods. Ancient Greeks are known for their black-figure and red-figure pottery, while ancient Chinese civilizations developed early forms of porcelain. Ceramics were not only functional but also served as a canvas for storytelling, with intricate scenes painted or etched onto their surfaces.
Metalworking and Goldsmithing
Metalworking allowed for the creation of jewelry, weapons, and ceremonial objects. Ancient Egyptian artisans, for instance, were highly skilled in goldsmithing, creating elaborate jewelry with precious stones. Mesopotamian and Mesoamerican artisans also developed advanced techniques for casting and molding metals, contributing to both decorative arts and functional items.
Textiles and Weaving
Textile arts were essential in ancient civilizations, where weaving was often done by hand using natural fibers. In Mesoamerica, textiles were dyed with vibrant colors and adorned with complex patterns. In ancient Egypt, linen was the primary material, and fine weaving became a specialized craft.
Cultural Significance of Ancient Art
Art in ancient civilizations was more than mere decoration—it was a vital part of religious, political, and social life. Through art, people communicated with deities, honored their leaders, and recorded historical events. Religious motifs are particularly prevalent, seen in the depiction of gods, goddesses, and mythological scenes across cultures. Art also served as a tool for political power, with rulers commissioning grand monuments and portraits to convey strength and divine favor.
Religion and Spirituality in Ancient Art
In many ancient societies, art was deeply connected to religious beliefs. Egyptian tomb paintings, for instance, were meant to guide the deceased in the afterlife, while Mayan carvings depicted the gods and cosmic events. Religious art often used symbolism to convey complex ideas, such as the Egyptian ankh symbolizing life or the lotus flower representing purity in Indian art.
Storytelling and Mythology
Ancient art also functioned as a means of storytelling, passing down myths, legends, and historical events. In Greek and Roman art, mythological scenes were common, often portraying the deeds of gods and heroes. Mesoamerican art frequently depicted creation myths and cosmological cycles, reflecting the spiritual beliefs of the people.
Power and Prestige
Rulers used art to reinforce their authority and divine right to rule. The grandiose statues of pharaohs in Egypt, the colossal figures of Mesopotamian kings, and the elaborate Roman triumphal arches all served to glorify leaders and legitimize their power. By commissioning monumental art, rulers could project their image and legacy far beyond their lifetime.
Legacy of Ancient Art in Modern Culture
The techniques, styles, and themes developed by ancient civilizations continue to influence contemporary art and architecture. Many modern artists draw inspiration from the past, incorporating classical techniques, symbolism, and materials. For example, the use of marble sculpture and architectural columns in neoclassical buildings evokes the legacy of ancient Greece and Rome.
Ancient art also provides a source of fascination and study in academia, where scholars explore the historical, cultural, and technical aspects of ancient artifacts. Museums and exhibitions allow people to experience these works firsthand, fostering a deeper appreciation for the art and achievements of ancient civilizations.
Ancient Art Techniques in Today’s Creative Process
Modern artists often study ancient techniques as a way of mastering foundational skills. Stone carving, fresco painting, and pottery continue to be practiced today, often with the same reverence for craftsmanship as ancient artists once had. The study of ancient art techniques provides not only insight into historical methods but also inspiration for contemporary artistic experimentation.
FAQs
What is the importance of studying ancient art?
Studying ancient art allows us to understand the values, beliefs, and innovations of early civilizations, offering insight into human creativity and the evolution of artistic expression.
How did ancient civilizations influence modern art?
Ancient civilizations contributed foundational techniques and themes that continue to influence modern art styles, symbolism, and architecture, from marble sculpture to fresco painting.
What were common materials in ancient art?
Ancient artists used materials such as stone, clay, metals, and natural pigments. Each civilization adapted its resources to create unique artworks suited to its environment and culture.
What role did religion play in ancient art?
Religion was central to ancient art, often dictating subject matter, symbolism, and purpose. Many artworks were created to honor gods, guide the dead, or convey spiritual beliefs.
How were ancient art techniques preserved?
Ancient art techniques were often passed down through generations or revived during periods like the Renaissance. Modern archaeologists and artists continue to study these techniques to preserve historical knowledge.
What are some famous examples of ancient art?
Some well-known examples include the Egyptian pyramids, the Greek Parthenon, the Roman Colosseum, Mayan pyramids, and the Chinese Terracotta Army.
Conclusion
Ancient art is a testament to human ingenuity and expression. From the monuments of Egypt to the temples of Greece, from the frescoes of Rome to the pottery of Mesoamerica, ancient civilizations left an indelible mark on art history. By studying ancient art and understanding its techniques, we gain a deeper appreciation for the creativity that has shaped human culture for millennia. Through these artistic treasures, the voices of the past continue to speak, inspiring and guiding us in the present.